

Psychotherapy: Also known as talk therapy or counseling, this treatment has been shown to help some patients with depression. Medications take time - usually 2 to 4 weeks - to work, and often symptoms such as appetite, concentration problems and sleep improve before people may notice mood changes, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. Other classes of antidepressants include serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), Norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs), Tricyclic antidepressants, and Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Side effects, which are usually temporary, include changes in sexual desire, digestive problems, headache, insomnia and nervousness. This class of medication includes fluoxetine (commonly known as Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), paroxetine (Paxil), escitalopram (Lexapro) and citalopram (Celexa). SSRIs target the brain's serotonin, a signaling chemical (neurotransmitter) that studies have found to be involved in depression. There are several categories of antidepressants, but doctors often start with a class of drugs called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and may try other medications if the patient's condition didn't improve. Medication: Prescription drugs, called antidepressants, help alter mood by affecting naturally occurring brain chemicals. According to the Mayo Clinic, these include alcohol or drug abuse, anxiety, social isolation and relationship conflicts, work or school difficulties, or suicide.ĭepression treatment may involve psychotherapy therapy, medications, or a combination of the two. Left untreated, major depression can set off a chain of social, emotional and health consequences that add to patients' overall stress. Surveys have shown that up to half of Americans with depression don't get medical help for their condition. So doctors may do a blood test, or test the thyroid to make sure it's functioning properly, according to the Mayo Clinic.Īnd lastly, doctors look at whether "the symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational or other important areas of functioning," according to the DSM.

It must also be ruled out that the symptoms are not caused by another medical condition, such as a thyroid problem, or due to the direct effects of a drug or medication. The person must also exhibit a depressed mood, or loss of interest or pleasure.
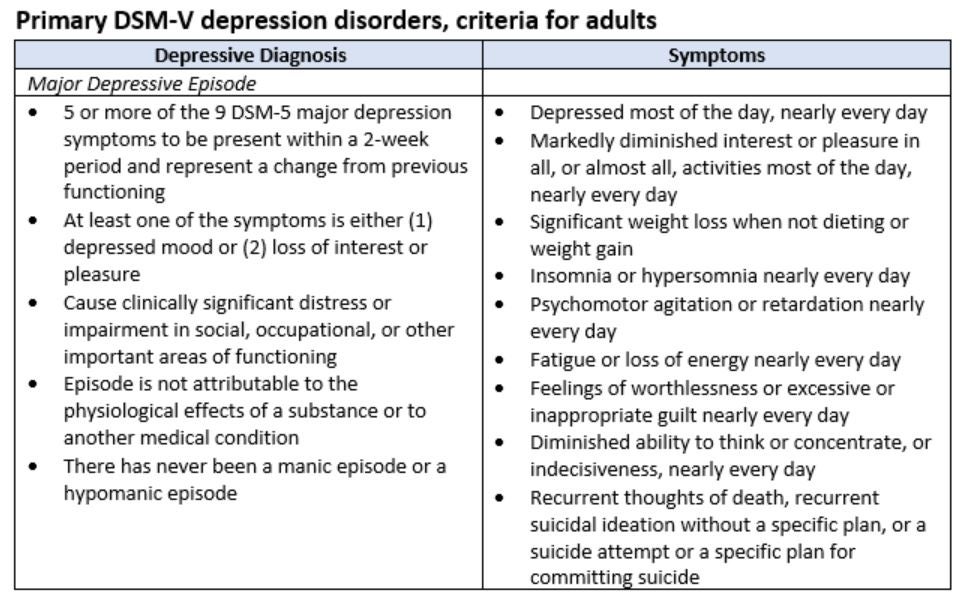
#Depression symptoms dsm 5 manual#
In the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), which is a mental health guidebook for doctors published by the American Psychiatric Association, to diagnose a person with major depressive disorder, the person must show five or more of the symptoms (listed above) for at least two weeks. They may also ask patients to report their depression symptoms on a printed questionnaire. To diagnose a person with depression disorder, doctors may ask patients about their family health history, mood and behavior patterns (such as eating and sleeping), and thoughts of suicide. Hormonally induced depression can arise after childbirth or at menopause as well.Īdditionally, some sedatives, such as sleeping pills, and high blood pressure medications are linked to depression, according to the NIH. Most likely, depression is caused by a combination of genetic, biological, environmental, and psychological factors, according to the NIMH.Ĭertain medical conditions may also trigger depression, including an underactive thyroid gland, cancer, heart disease, prolonged pain and other significant illnesses. Moreover, a variety of distressing life situations are also associated, including early childhood trauma, a job loss, the death of a loved one, financial troubles or a divorce.
However, there are several theories about what this imbalance actually is and which signaling chemicals are involved. The causes of depression are not fully understood, but scientists think that an imbalance in the brain's signaling chemicals may be responsible for the condition in many patients. Withdrawal from social situations and normal activities.Unexplainable physical symptoms such as headaches or body aches.Change in appetite and/or weight, eating too much or too little.Inability to focus, concentrate or make decisions.Irritability, agitation or restlessness.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
